2019 Unofficial Defcon DFIR CTF Writeup - Linux Forensics
When completing this portion of the CTF I relied upon Autopsy 4.12 heavily, using the CTF as an opportunity to practice and trial a different toolset/ approach. In general I was impressed, but I’m not an Autopsy user day to day and as such I was fumbling a fair bit. For the Linux portion of the challenge, in hindsight, I think mounting the image within a Linux distribution would make more sense. For that reason, in this writeup I have addressed how to solve the questions using SIFT.
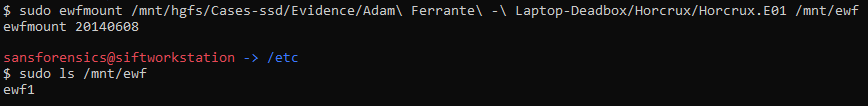
You can mount the image under sift, using the ewfmount command:
sudo ewfmount /mnt/hgfs/Cases-ssd/Evidence/Adam\ Ferrante\ -\ Laptop-Deadbox/Horcrux/Horcrux.E01 /mnt/ewf
The new file object is named ewf1:
This presents the E01 as a raw file which can the be mounted with a loopback device. First, we need to establish where the partition of interest is located and to achieve this I use ‘mmls’:
mmls /mnt/ewf/ewf1
This provides the below output:
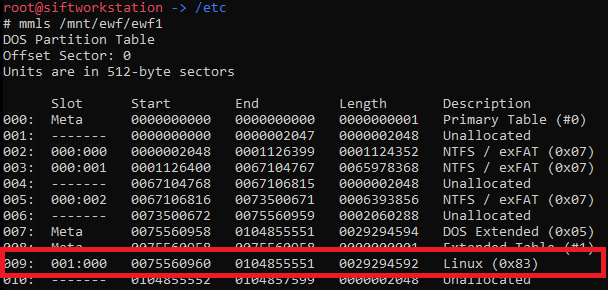
We can see that “Units are in 512-byte sectors” and that the start offset of the Linux partition is 75560960. Multiplying these together we get ‘38687211520’ which is the byte offset we will use for mounting the partition. First I created a directory to use as a mount point, with:
mkdir /mnt/linux_mount
Then using the mount command, we can mount the partition read only:
mount -o ro,loop,offset=38687210496 -t ext4 /mnt/ewf/ewf1 /mnt/linux_mount
Or not…
The error above can result from a number of things, however in this case it is because the filesystem is dirty. When mounting the drive it attempts to rectify the issue, which cannot be performed with a read only mount. We can overcome this issue by passing the ‘norecovery’ option when mounting:
mount -o ro,norecovery,loop,offset=38687211520 -t ext4 /mnt/ewf/ewf1 /mnt/linux_mount
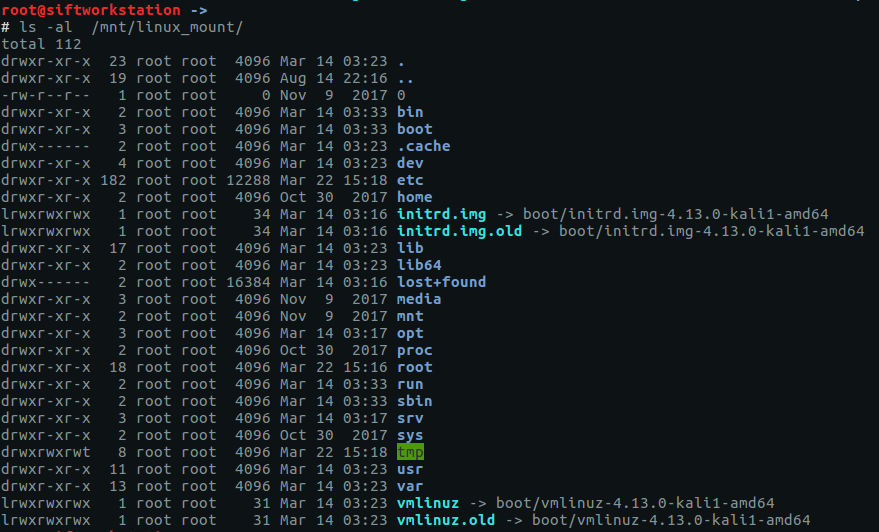
This worked without error and if we 'ls' the new mountpoint we can see that we now have access to the mounted filesystem:
Now we have the filesystem mounted... on with the questions!
red star - 10 pts
Question
What distribution of Linux is being used on this machine?
Answer
There are various ways to determine the distribution in use within a linux install/image. When looking at a dead image checking the contents of /etc/issue, /etc/*-version or /etc/*_version is the quickest and easiest.
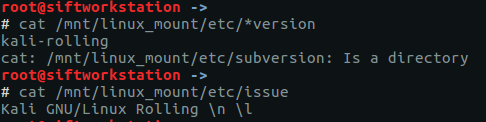
A simple cat of /mnt/linux_mount/etc/*version or /mnt/linux_mount/etc/issue provides the following:
Throughout this process be careful to ensure you are targeting the mounted filesystem and not your analysis system's filesystem. I will normally navigate to the root of the target and work from there as my working directory, in this case using ‘cd /mnt/linux_mount’. Thereafter a path in the OS under analysis would be equivalent to that of being at the root of the system and we can presceed any paths with '.' to indicate that we should be starting from the current directory. the current director.e.g.:
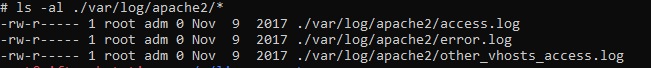
cat ./var/log/apache2/access.log
Due to my working from the route of the mounted drive the command above will target '/mnt/linux_mount/var/log/apache2/access.log' on my analysis system.
Going back to the screenshot and the output of our commands, it looks like we are dealing with Kali.
flag<Kali>
abc123 - 10 pts
Question
What is the MD5 hash of the apache access.log?
Answer
By default the apache access log is located at /var/log/apache2/access.log. So with a working directory of the root of the mounted fs, we can use:
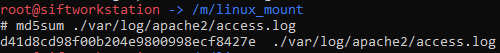
md5sum ./var/log/apache2/access.log
Which provides the following:
flag<d41d8cd98f00b204e9800998ecf8427e>
Radiohead - No Surprises - 10 pts
Question
It is believed that a credential dumping tool was downloaded? What is the file name of the download?
Answer
As a first step in familiarising myself with the image I reviewed the ‘/etc/passwd’ file in an effort to see what users were active and worthy of further investigation. With regard to this specific questions I was particularly interested to see which users had home directories as possible locations to have downloaded files to.
As is default in kali, the 'root' account is the only user account, and the home directory was at ‘/root’. A quick way of having an easy to review list of home directories in use is to use the following command:
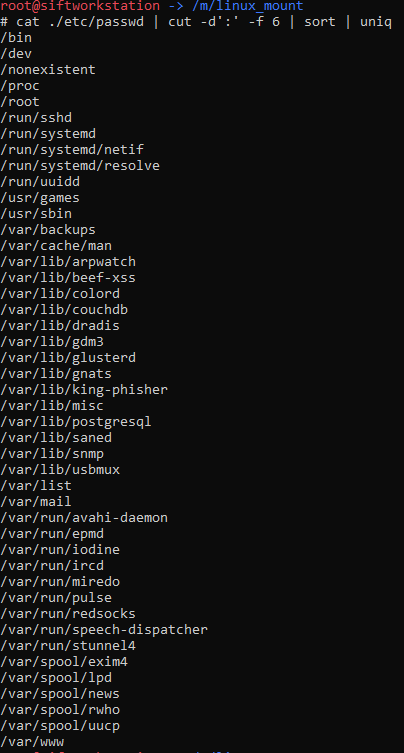
cat ./etc/passwd | cut -d':' -f 6 | sort | uniq
Which results in this output:
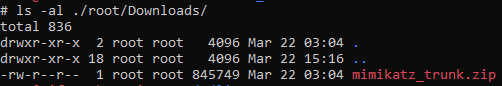
Based on the above we will start with the ‘root’ user and it makes sense to check on the contents of the associated ‘Downloads’ folder:
ls -al ./root/Downloads/
Which results in the below:
Only one file, and it’s filename is sure does look like that of a well-known credential dumping tool.
flag<mimikatz_trunk.zip>
super duper secret - 15 pts
Question
There was a super secret file created, what is the absolute path?
Answer
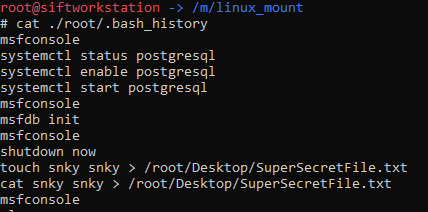
Within the bash history for ‘root’ (/root/.bash_history) we see that someone piped the output of a cat command into ‘/root/Desktop/SuperSecretFile.txt’:
flag</root/Desktop/SuperSecretFile.txt>
this is a hard one - 15 pts
Question
What program used didyouthinkwedmakeiteasy.jpg during execution?
Answer
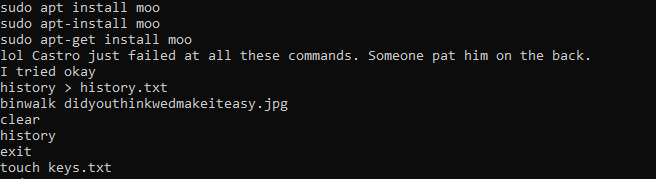
Still in the bash history we see ‘binwalk’ being used over didyouthinkwedmakeiteasy.jpg:
flag<binwalk>
overachiever - 15 pts
Question
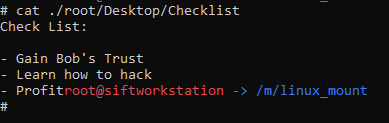
What is the third goal from the checklist Karen created?
Answer
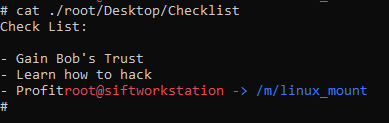
There is a file on the desktop for ‘root’ called ‘Checklist’, reviewing its content we see that it has three items:
flag<Profit>
attack helicopter - 20 pts
Question
How many times was apache run?
Answer
We earlier reviewed the apache access log to calculate its hash, and the eagle eyed forensicators among us may have noticed that the hash was ‘d41d8cd98f00b204e9800998ecf8427e’ which is the MD5 associated with a 0 byte file.
Reviewing the log directory, we find the same to be true of the other logs:
Most notable is the error.log as this log is populated with entries upon apache starting. Assuming the log hasn’t been tampered with, it being empty is an indication that apache has not run.
flag<0>
oh no some1 call ic3 - 25 pts
Question
It is believed this machine was used to attack another, what file proves this?
Answer
While spelunking through the image to get my bearings, I happened upon a screenshot within the home directory for ‘root’. This file is located at ‘/root/irZLAohL.jpeg’ and is reproduced below:
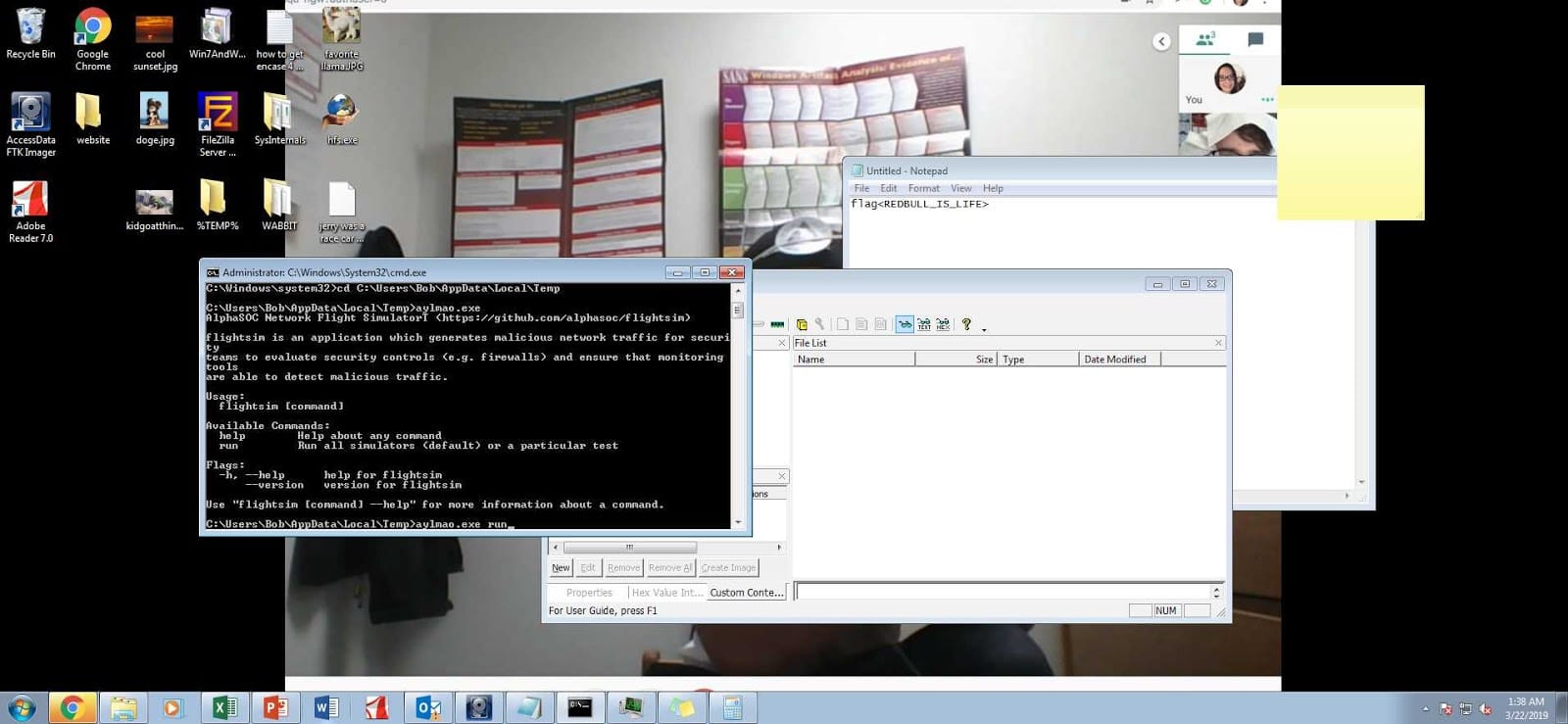
Notably this image contains a screenshot of a windows host, probably captured during a malicious remote access session. The filename was accepted as the flag. Further notable is that the screenshot includes the notepad window open with a flag which we had previously found in the Triage Memory questions. It’s all starting to fall into place…
flag<irZLAohL.jpeg>
scripters prevail - 25 pts
Question
Within the Documents file path, it is believed that Karen was taunting a fellow computer expert through a bash script. Who was Karen taunting?
Answer
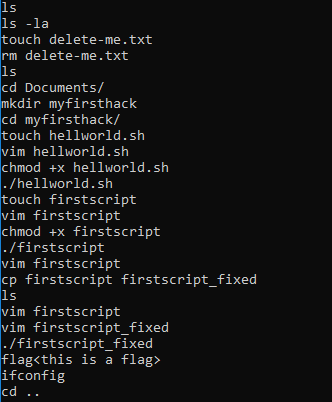
When reviewing bash history we saw various references to bash scripts:
Reviewing that excerpt we see that the user navigated to ‘Documents’, made a directory called ‘myfirsthack’, entered that directory and then created, modified, chmod’d and executed two scripts (hellworld.sh and firstscript), they then copied firstscript to firstscript_fixed and executed it. Lets see what they contain:
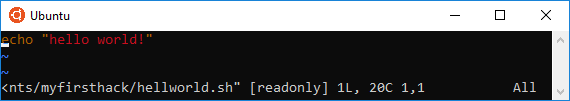
Not so interesting, and:
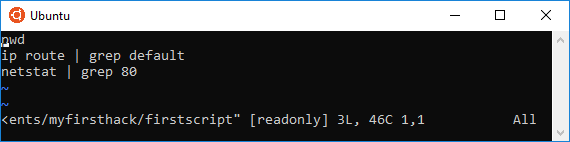
Nope, third time is a charm?:
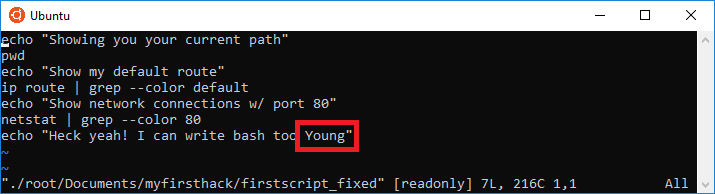
Here we have a reference to a ‘Young’, lets give that a go!
flag<Young>
the who - 30 pts
Question
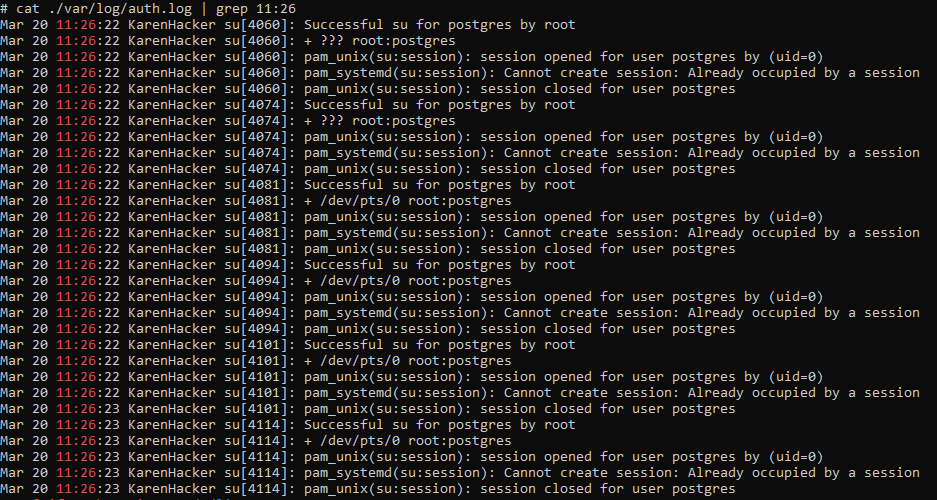
A user su'd to root at 11:26 multiple times. Who was it?
Answer
su events are recorded in the auth log at ‘/var/log/auth.log’, we can quickly parse this for events at that time using the following:
cat ./var/log/auth.log | grep 11:26
This gives us the following output:
And we can see that user ‘postgres’ has multiple entries that minute stating “Successful su for postgres by root”.
flag<postgres>
/ - 30 pts
Question
Based on the bash history, what is the current working directory?
Answer
Within the bash history, reviewing the last cd to an absolute path we see that the user changed directory to /root. Thereafter we can review the following cd commands to see what impact they would have on the current working directory.
| Command | Resultant Working Directory |
|---|---|
| cd /root | /root |
| cd ../root | /root |
| cd ../root/Documents/myfirsthack/../../Desktop/ | /root/Desktop |
| cd ../Documents/myfirsthack/ | /root/Documents/myfirsthack |
So we see the final state is '/root/Documents/myfirsthack'
flag</root/Documents/myfirsthack>